The United Indian

On August 28, 2024, a landmark decision by India’s Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs (CCEA) set the stage for a transformative era in urban and industrial development. Under the leadership of Prime Minister Narendra Modi, the Indian government approved 12 new smart city projects, marking a significant expansion of the National Industrial Corridor Development Programme (NICDP). This ambitious initiative, with an investment of INR 286.02 billion (US$3.41 billion), promises to reshape India’s economic landscape, strengthen manufacturing capabilities, and create millions of job opportunities.
Understanding Smart Cities: A Vision for the Future
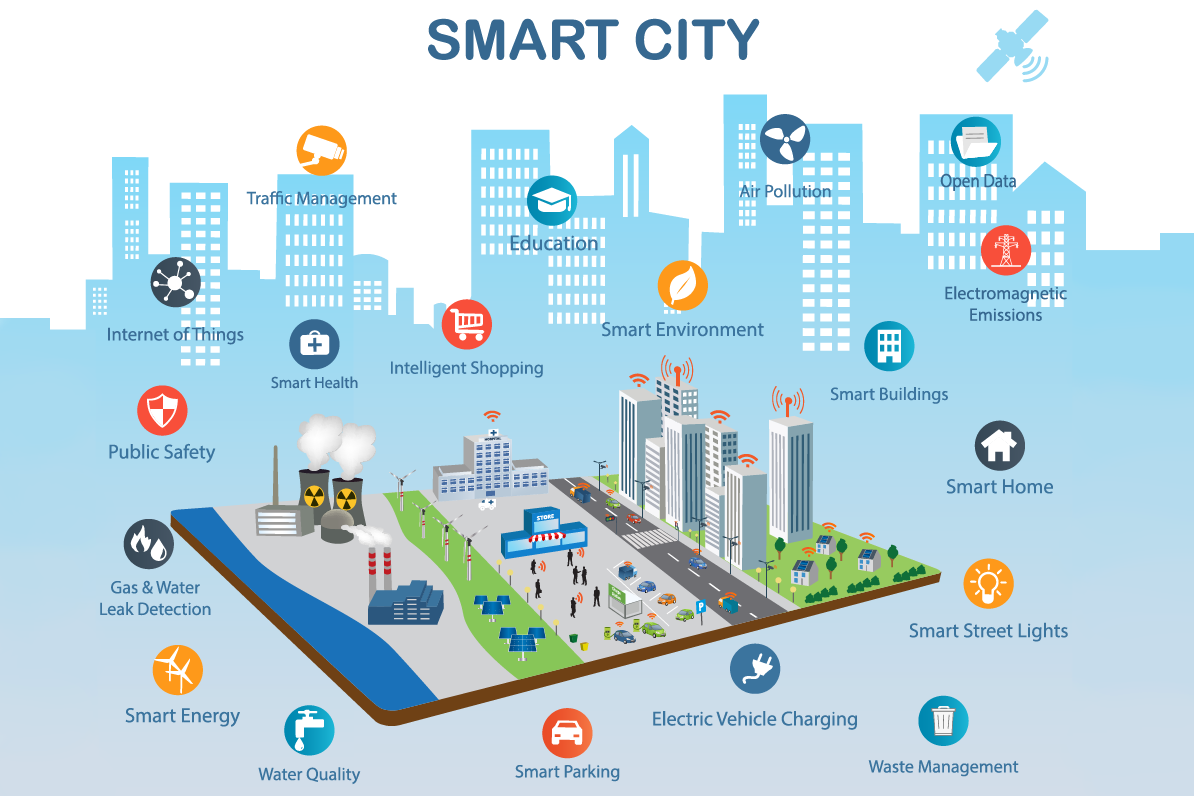
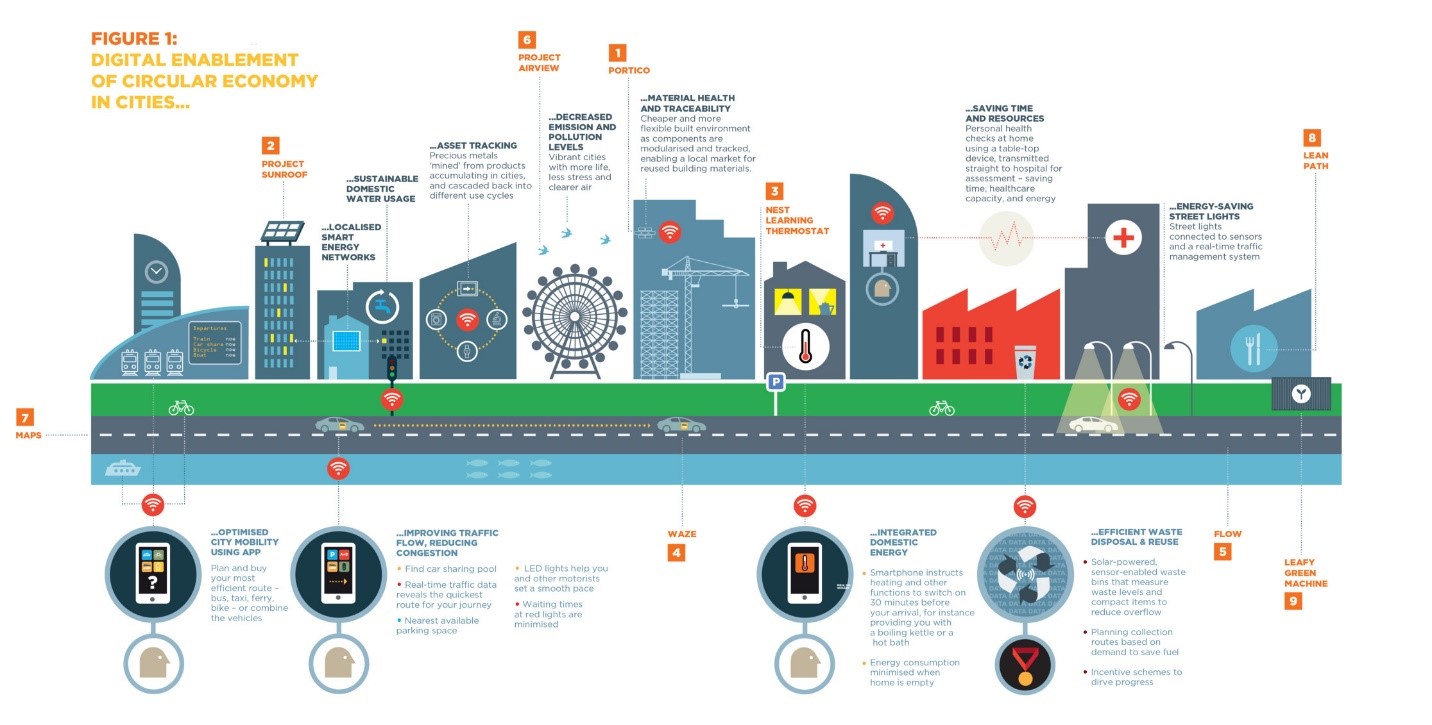
At their core, smart cities represent an evolution of urban planning. They are designed to integrate technology and data to enhance the quality of life for residents, improve infrastructure efficiency, and foster sustainable development. The concept revolves around using innovative technologies to manage and optimize city operations—from transportation and energy management to waste disposal and public services.
In the context of India’s latest initiative, these smart cities are envisioned as high-tech industrial hubs. They are not just about digital infrastructure but also about creating environments that support advanced industries, attract global investments, and boost economic activities. These cities aim to serve as focal points for India’s economic growth by integrating modern infrastructure with sustainability principles.
The 12 New Smart Cities: Locations and Goals
The newly sanctioned 12 industrial smart cities in India are strategically located across various states in India, each selected for its potential to drive regional and national growth. The 12 cities include:
- Khurpia, Uttarakhand
- Rajpura-Patiala, Punjab
- Dighi, Maharashtra
- Palakkad, Kerala
- Agra and Prayagraj, Uttar Pradesh
- Gaya, Bihar
- Zaheerabad, Telangana
- Orvakal and Kopparthy, Andhra Pradesh
- Jodhpur-Pali, Rajasthan
An additional location remains undisclosed due to election-related regulations in certain states.
These cities will be developed as “smart industrial hubs,” a concept that blends high-tech infrastructure with economic functionality. Each city is designed to be a modern industrial center focusing on sectors like technical textiles, electric vehicles, aero logistics, food processing, and tourism. The NICDP envisions these hubs as drivers of substantial economic activities, contributing to India’s goal of achieving US$2 trillion in exports by 2030.
Economic Impact and Employment Opportunities
The scale of investment and the expected economic impact of these smart cities are enormous. The total investment of INR 286.02 billion is projected to attract an additional INR 1.52 trillion (US$18.12 billion) from both large industries and micro, small, and medium enterprises (MSMEs). This influx of investment is anticipated to create 1 million direct jobs and 3 million indirect jobs, significantly reducing unemployment and fostering economic development in these regions.
Piyush Goyal, India’s Commerce and Industry Minister, has described this initiative as a “necklace of industrial cities” connected by the Golden Quadrilateral national highway network, enhancing logistics and connectivity across the country. This network is designed to support seamless movement of goods and services, vital for economic integration and growth.
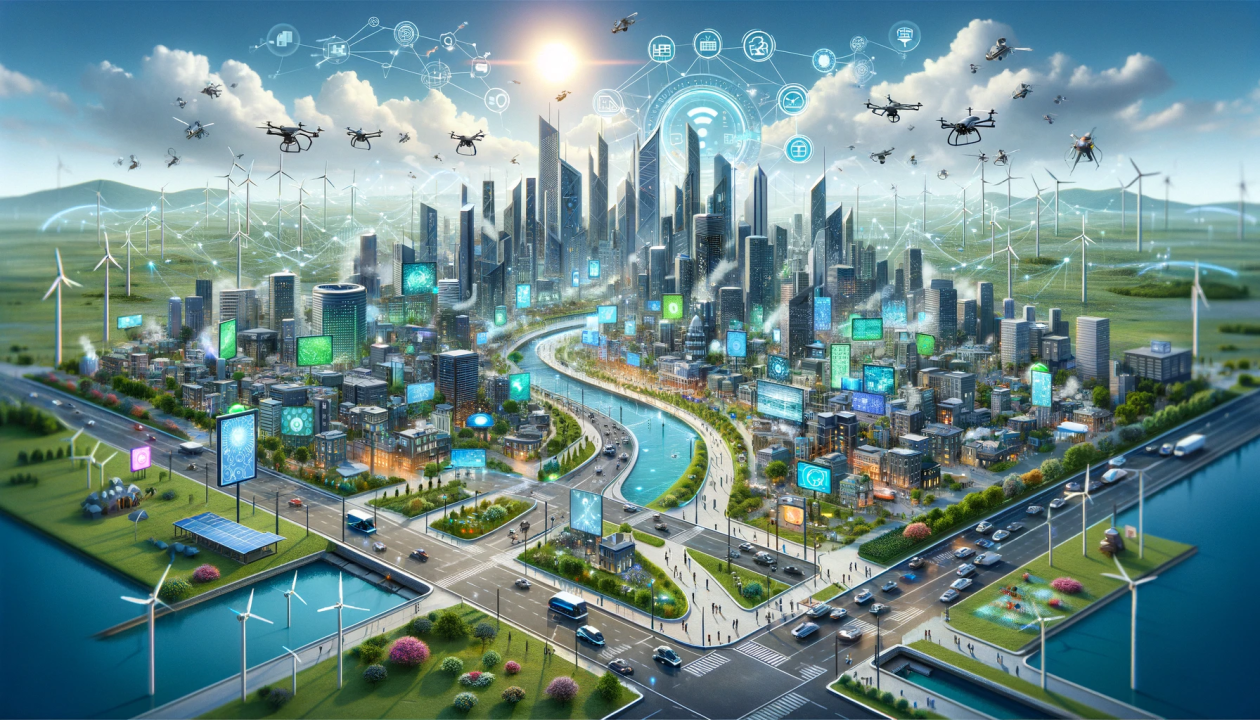
Technological Integration: Smart Features and Sustainability
The smart cities under NICDP will feature state-of-the-art technological solutions and sustainable practices. Key elements include:
- Plug-and-Play Infrastructure: This concept allows businesses to quickly set up operations with minimal setup time, offering pre-built facilities and services tailored to industry needs.
- Walk-to-Work Design: Urban planning will emphasize proximity between residential and industrial areas, reducing commute times and enhancing the overall quality of life.
- Sustainability Practices: Each city will incorporate eco-friendly practices, such as renewable energy sources, efficient waste management systems, and green spaces, aligning with global sustainability goals.
Railway Projects and Hydro-Power Initiatives
In addition to the smart cities in India, infrastructure development includes significant investments in railway and hydro-power projects. The CCEA approved INR 64.56 billion (US$769.9 million) for three major railway projects designed to enhance logistics across four states—Odisha, Jharkhand, West Bengal, and Chhattisgarh. These projects include new railway lines and multi-tracking initiatives, crucial for transporting essential commodities and improving regional connectivity.
Furthermore, a substantial equity support of INR 41.36 billion (US$493.2 million) has been allocated for hydro-power projects in India’s northeastern states. These projects, with a total capacity of 15,000 MW, aim to upgrade power infrastructure, support economic growth, and promote environmentally sustainable practices.
The Broader Vision: Integration with PM GatiShakti Master Plan
The smart city projects are part of India’s broader strategy under the PM GatiShakti National Master Plan. This plan seeks to provide integrated multi-modal connectivity to improve the efficiency of logistics and transportation networks. By aligning these smart city initiatives with the GatiShakti plan, India aims to create a cohesive and interconnected infrastructure system that supports economic development and global competitiveness.
Conclusion
India’s investment in smart cities and related infrastructure projects signifies a pivotal moment in the country’s development trajectory. By creating modern, sustainable industrial hubs and enhancing transportation and energy infrastructure, India is positioning itself as a global player in manufacturing and economic growth. These initiatives promise not only to bolster the country’s economic landscape but also to set a benchmark for smart urban development worldwide. As these projects unfold, they will likely become models for how technology and infrastructure can work together to create more efficient, sustainable, and prosperous cities.
Read more in Government Sector
Jul 11, 2025
TUI Staff
Jul 09, 2025
TUI Staff
May 28, 2025
TUI Staff

Stay Tuned with The United Indian!
Our news blog is dedicated to sharing valuable and pertinent content for Indian citizens. Our blog news covering a wide range of categories including technology, environment, government & economy ensures that you stay informed about the topics that matter most. Follow The United Indian to never miss out on the latest trending news in India.
©The United Indian 2024