The United Indian

We have been time and again focusing on issues concerning Climate Change.
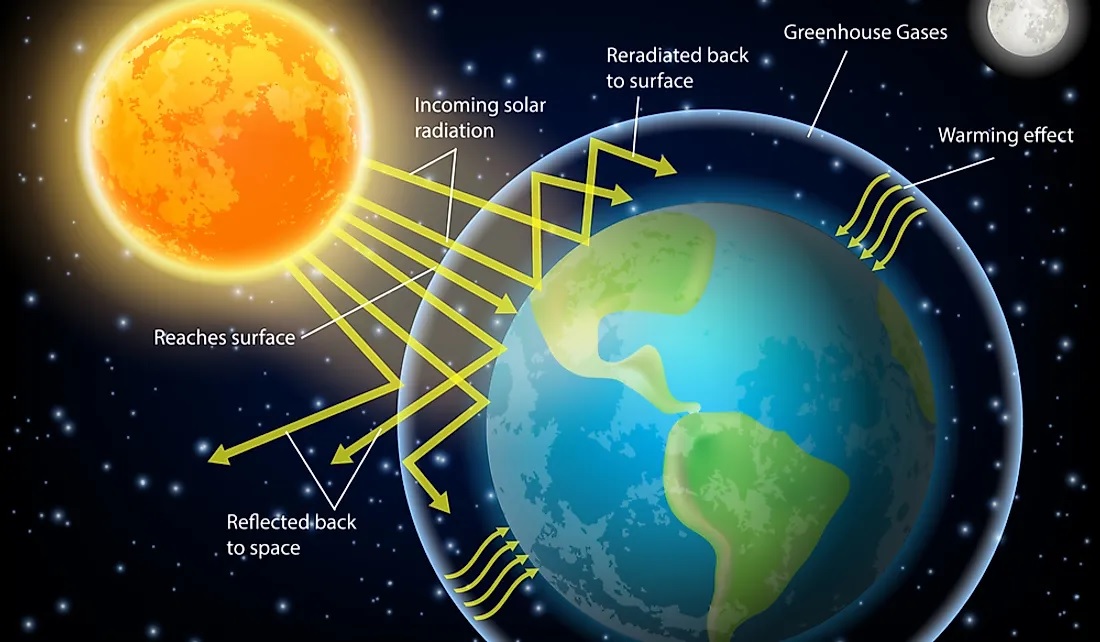
The reason : Climate change is one of the most pressing issues facing our planet today. The effects of which are already being felt around the world, in the form of more extreme weather events, rising sea levels, and changes in agricultural yields.
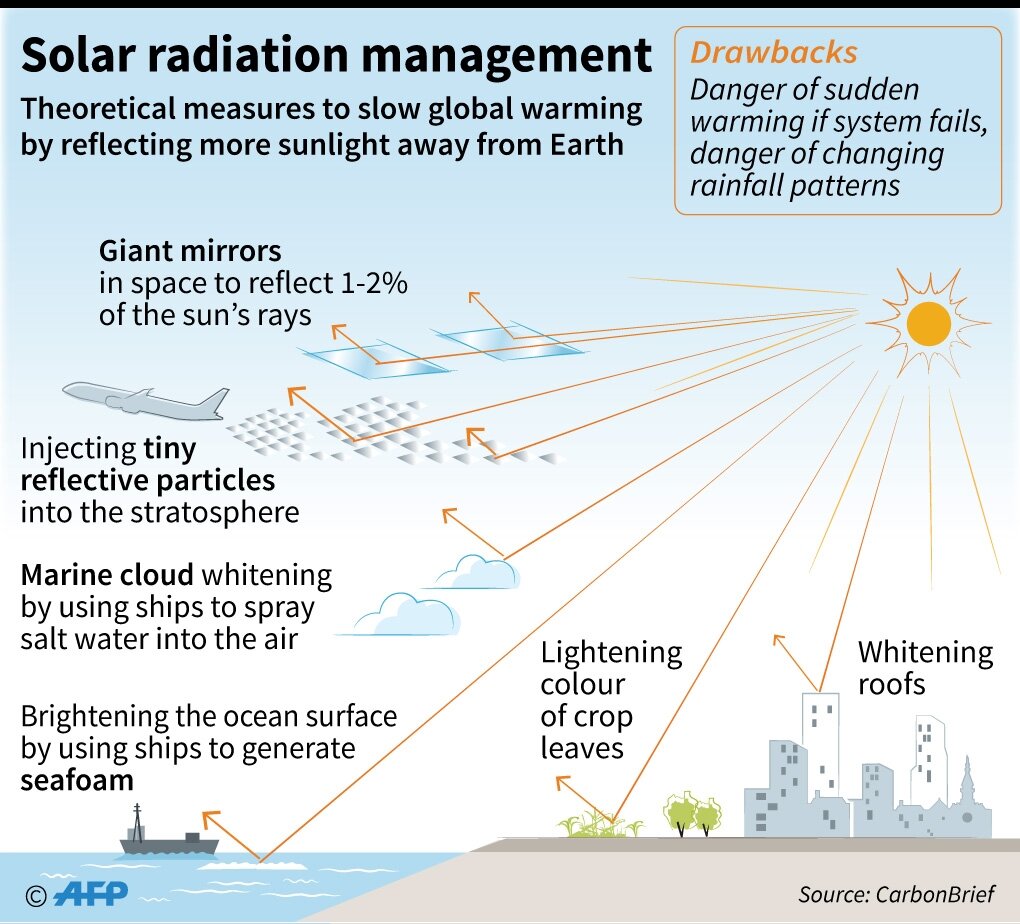
In recent years, there has been increasing interest in a controversial approach to climate change mitigation called Solar Radiation Management (SRM). SRM is a type of geoengineering that seeks to reduce the amount of solar radiation reaching the Earth's atmosphere. This can be done by injecting sulfate aerosols into the stratosphere, brightening marine clouds, or deploying space mirrors.
The potential benefits of SRM are significant. It could potentially slow or even reverse the effects of climate change, giving us more time to transition to a low-carbon economy. However, SRM also has a number of risks, including the potential to disrupt the Earth's climate system, create new environmental problems, and be used as a weapon.
In this blog post, we will explore the pros and cons of SRM, and discuss whether it could be the answer to climate change.
What is Solar Radiation Management?
Solar Radiation Management (SRM) is a type of geoengineering that seeks to reduce the amount of solar radiation reaching the Earth's atmosphere. This can be done by injecting sulfate aerosols into the stratosphere, brightening marine clouds, or deploying space mirrors.
The idea behind SRM is to mimic the effects of a volcanic eruption. When a volcano erupts, it releases sulfate aerosols into the stratosphere. These aerosols reflect sunlight back into space, cooling the Earth's surface.
SRM could potentially be used to offset the effects of climate change. By reducing the amount of solar radiation reaching the Earth, SRM could help to slow the rate of global warming.
How does Solar Radiation Management work?
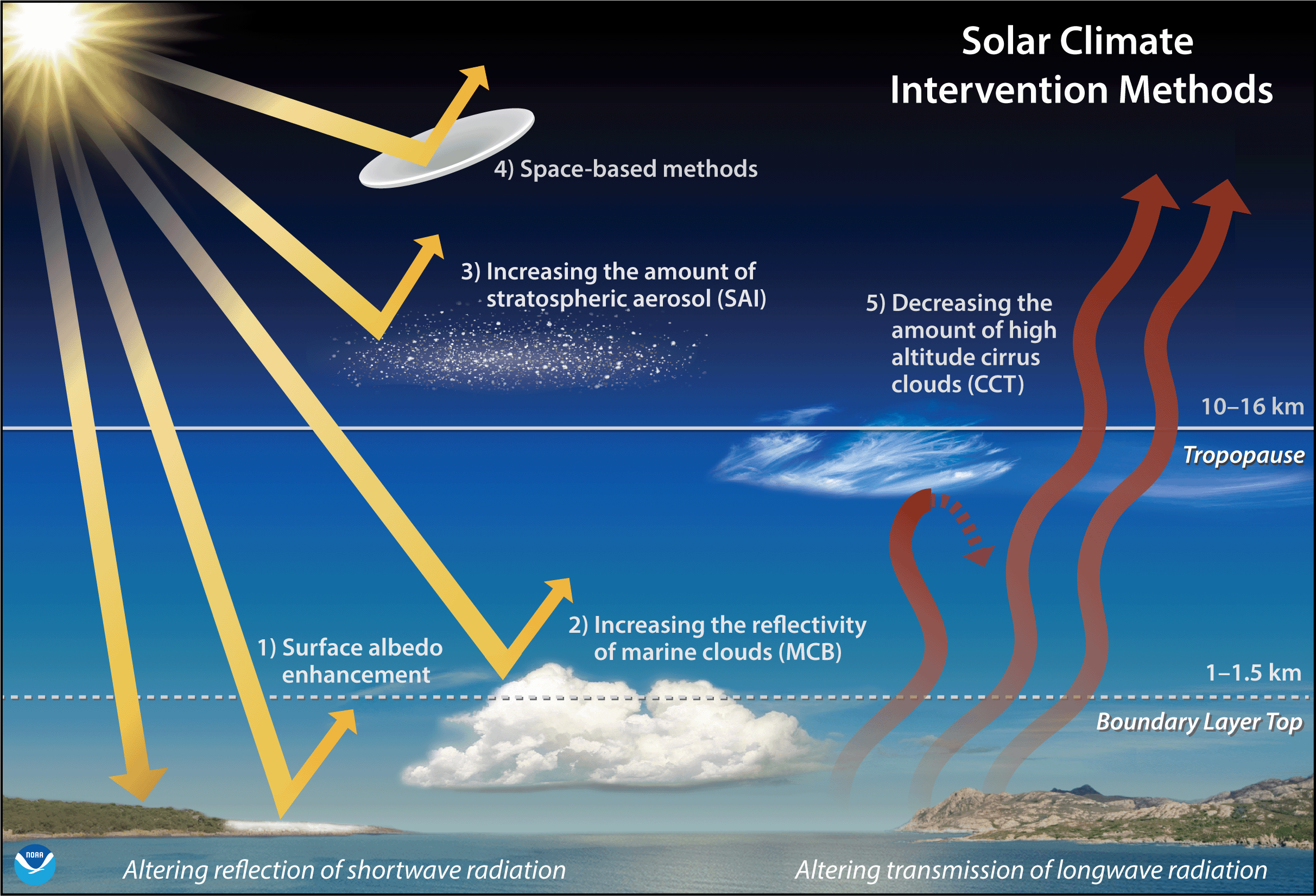
There are three main methods of SRM:
- Stratospheric aerosol injection (SAI): This involves injecting sulfate aerosols into the stratosphere. Sulfate aerosols are very good at reflecting sunlight, so they can effectively cool the Earth's surface. However, SAI could also have a number of negative environmental impacts, such as disrupting the ozone layer and the global monsoon system.
- Marine cloud brightening (MCB): This involves adding reflective particles to marine clouds. This can make the clouds brighter, which reflects more sunlight back into space. MCB is a relatively safe and low-cost method of SRM, but it is not as effective as SAI.
- Space mirrors: This involves deploying large mirrors in space to reflect sunlight away from the Earth. Space mirrors are the most effective method of SRM, but they are also the most expensive and technically challenging.
The Pros and Cons of Solar Radiation Management
Benefits of Solar Radiation Management
The potential benefits of SRM are significant. These include
- Temperature Reduction: One of the primary benefits of SRM is its ability to quickly reduce global temperatures. By reflecting a portion of the sun's energy away from the Earth's surface, SRM could provide a temporary cooling effect, helping to counteract the warming caused by greenhouse gas emissions.
- Rapid Response: In the face of sudden and severe climate events, such as heatwaves or extreme storms, SRM could offer a rapid response to stabilize temperatures. This could provide a valuable tool for emergency situations, potentially preventing or alleviating the worst impacts of such events.
- Affordability: Compared to some other large-scale interventions to address climate change, SRM might be relatively affordable to implement. This cost-effectiveness could make it an attractive option for countries and organizations seeking immediate solutions to reduce global warming.
- Adjustable Interventions: SRM techniques can be adjusted in terms of scale and intensity. This adaptability allows for a degree of control over the level of solar radiation reflected, enabling fine-tuning based on changing climate conditions and scientific understanding.
- Global Application: The implementation of SRM would have a global reach. This universality could potentially allow for coordinated international efforts to counteract the impacts of climate change, fostering collaboration and shared responsibility.
- Buy Time for Mitigation: While not a substitute for greenhouse gas emissions reduction, SRM could buy time for the development and implementation of longer-term mitigation strategies. It could provide a buffer period to transition to a low-carbon economy and develop sustainable practices.
- Technological Advancements: Research into SRM could drive advancements in various scientific and technological fields. As scientists explore new methods of reflecting sunlight, it could lead to innovative solutions and insights that have broader applications beyond climate management.
Drawbacks of Solar Radiation Management
SRM also has a number of risks. These risks include:
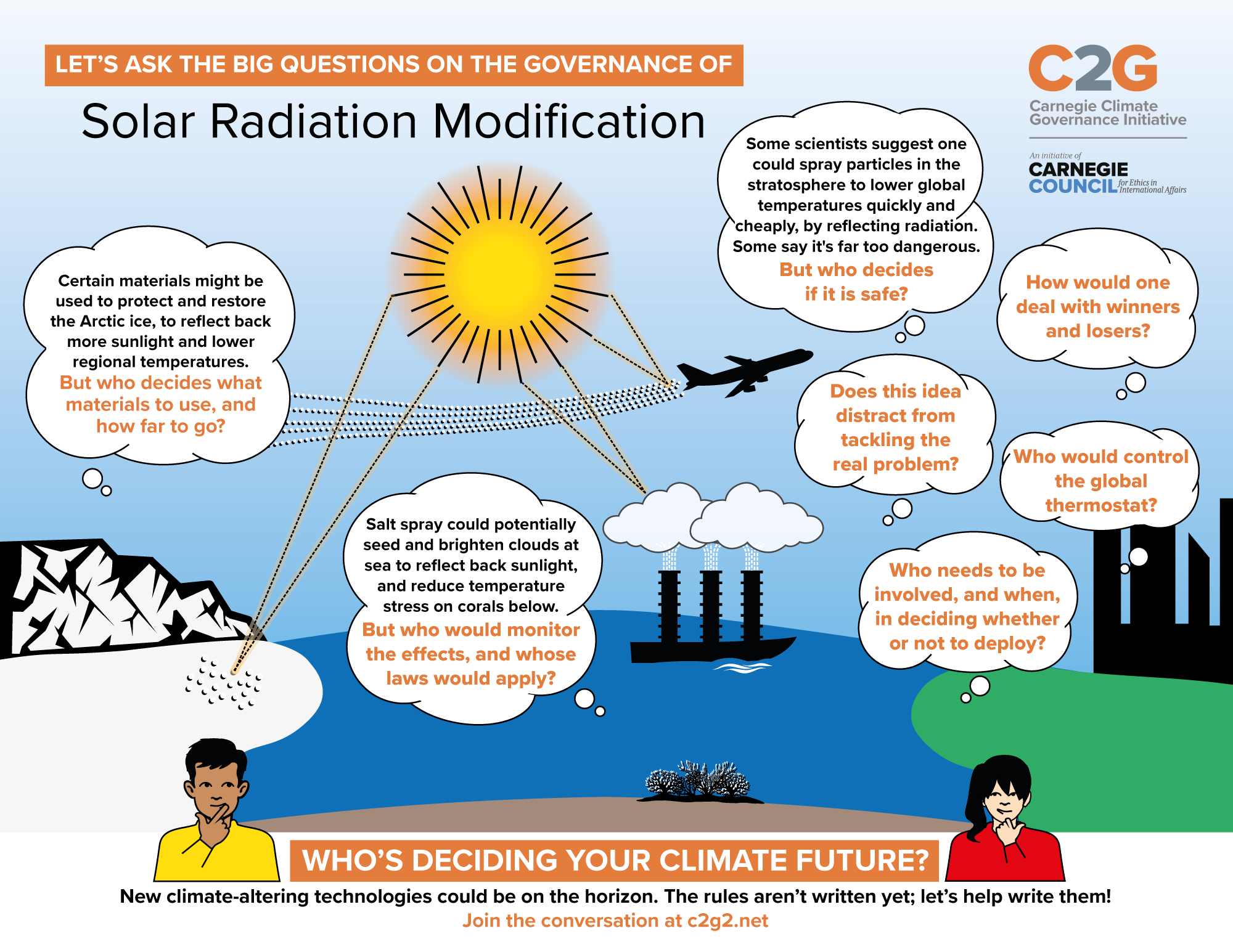
- Unintended Consequences: Introducing large quantities of reflective particles into the atmosphere could lead to unpredictable and potentially harmful consequences. Changes in weather patterns, precipitation distribution, and ozone layer depletion are concerns that need thorough examination.
- Environmental impacts: SRM could have a number of negative environmental impacts, such as disrupting the ozone layer, the global monsoon system, and the Earth's climate system.
- Ethical and Governance Challenges: Implementing Solar Radiation Management raises ethical questions about who should have the authority to make decisions about modifying the Earth's climate. Lack of international consensus and proper governance could lead to diplomatic tensions.
- Dependency on Continued Application: SRM does not address the root causes of climate change, such as greenhouse gas emissions. Continued reliance on Solar Radiation Management could delay efforts to transition to more sustainable energy sources.
The Future of Solar Radiation Management
The future of SRM is uncertain. There is still much research to be done on the potential benefits and risks of SRM. It is also unclear whether SRM will be politically acceptable.
However, SRM is a potential tool that could be used to mitigate the effects of climate change. If the risks of SRM can be mitigated, and if it is politically acceptable, then SRM could play a role in the future of climate change mitigation.
Conclusion
Solar Radiation Management is a controversial technology with the potential to both mitigate and exacerbate climate change. It is important to carefully consider the pros and cons of SRM before deciding whether or not to pursue it.
Only time will tell whether SRM will be the answer to climate change. However, it is a technology that deserves serious consideration as we work to mitigate the effects of climate change.
Read more in Environment
Oct 22, 2024
TUI Staff
Sep 10, 2024
TUI Staff

Stay Tuned with The United Indian!
Our news blog is dedicated to sharing valuable and pertinent content for Indian citizens. Our blog news covering a wide range of categories including technology, environment, government & economy ensures that you stay informed about the topics that matter most. Follow The United Indian to never miss out on the latest trending news in India.
©The United Indian 2024