The United Indian

India is a land of vibrant ecosystems & incredible biodiversity, home to a remarkable array of flora and fauna. However, many of these species are facing the threat of extinction due to various human-induced factors. In this article, we will explore some of the endangered species in India, the reasons behind their dwindling numbers, the government's efforts to protect them, and how we, as individuals, can contribute to their conservation.
Endangered Species in India
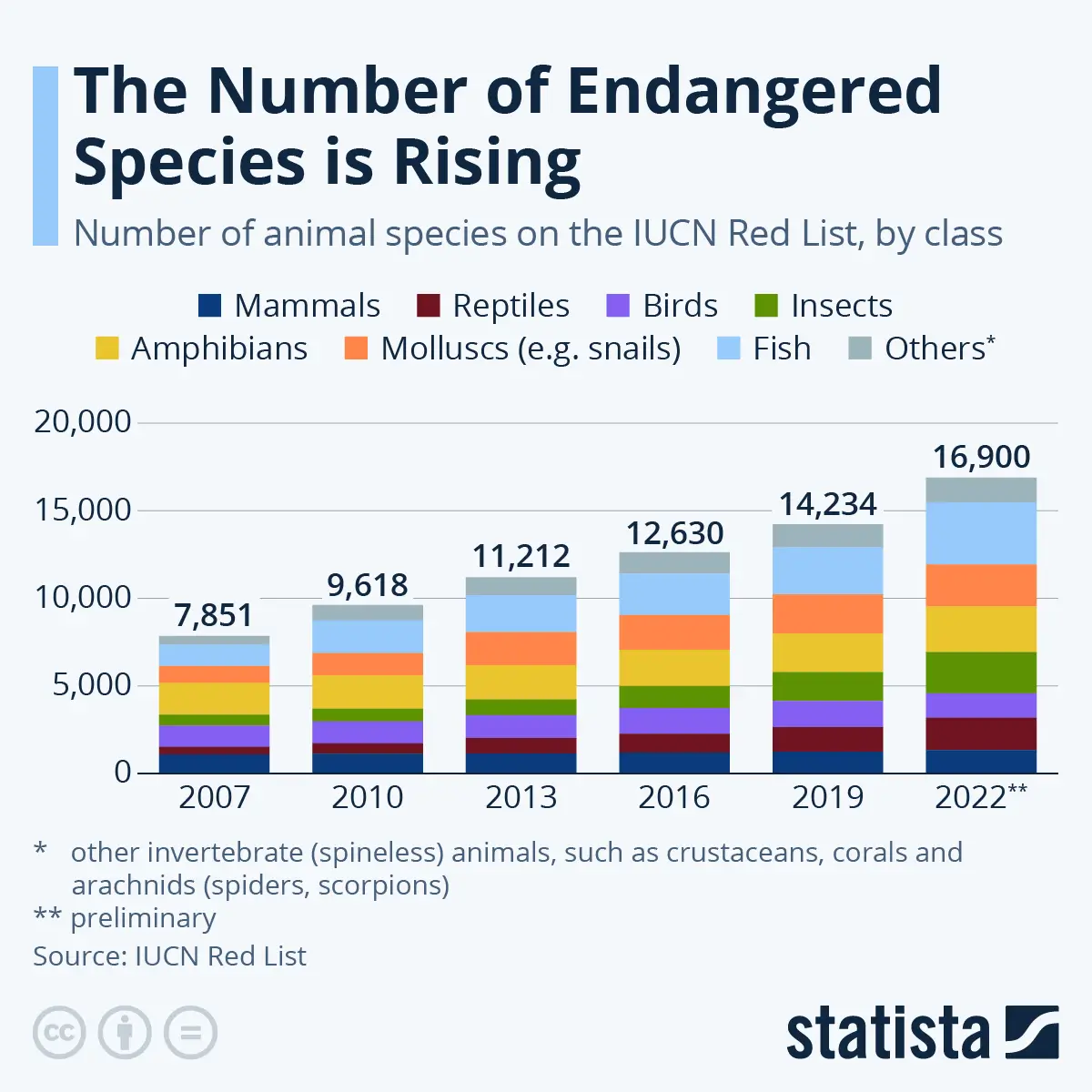
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List serves as a benchmark for the global conservation status of plant and animal species. In India, a multitude of species find themselves classified as Critically Endangered, Endangered, or Vulnerable on this list. Let's meet some of these fascinating creatures:
- Bengal Tiger (Panthera tigris tigris): The majestic Bengal tiger is considered the national animal of India & India boasts a whopping over 70% of the world's remaining wild tiger population. However, its population has declined dramatically due to habitat loss, poaching, and human-wildlife conflicts. About 5,574 tigers remain in the wild, according to the Global Tiger Forum (Data Source : https://www.worldwildlife.org/species/tiger)
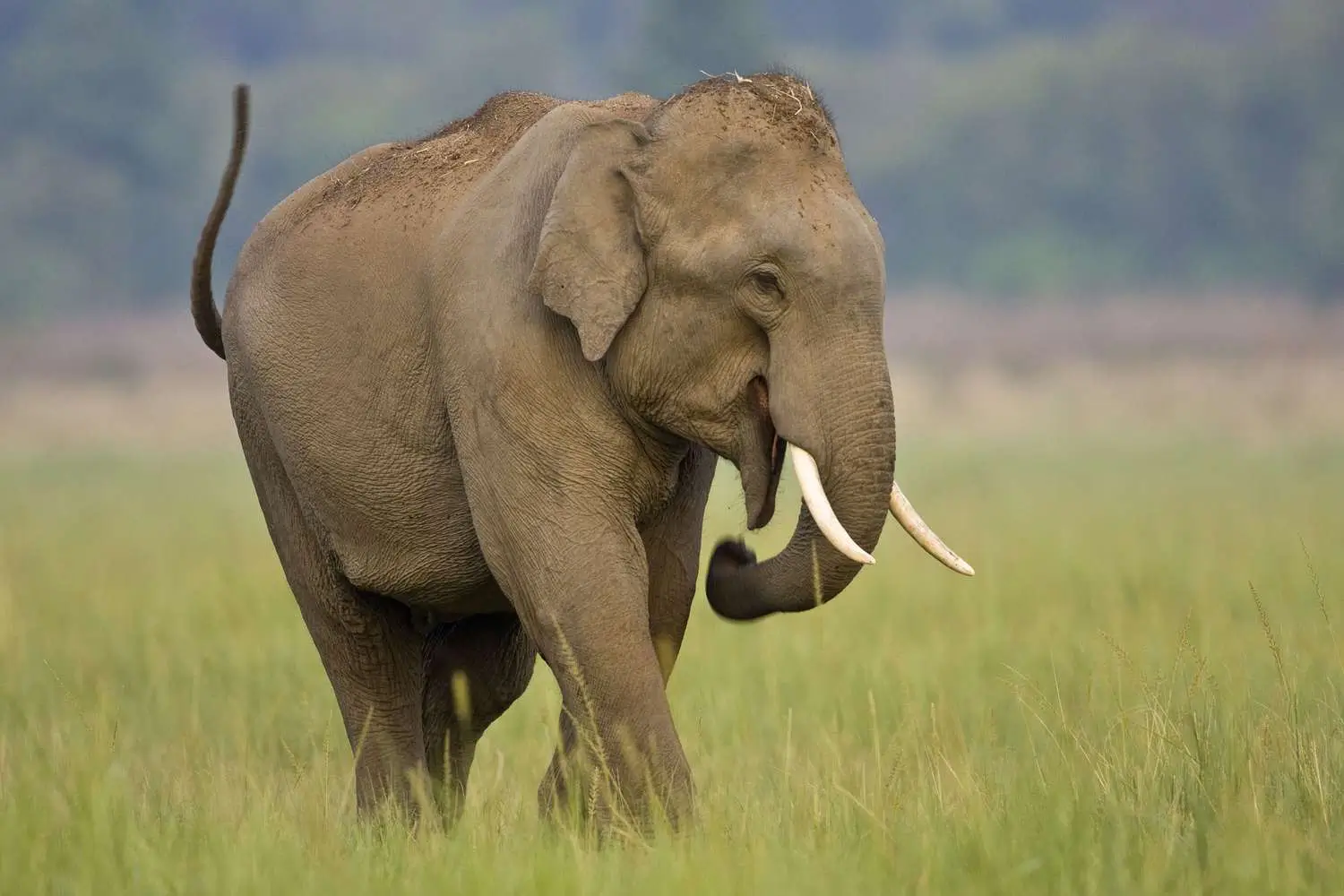
- Asian Elephant (Elephas maximus indicus): The Asian elephant is an iconic species in India, revered for its cultural significance. Unfortunately, habitat fragmentation, human-elephant conflicts, and illegal poaching for ivory have put immense pressure on their population. Current estimates suggest there are around 27,000 Asian elephants remaining in the wild.
3. Great Indian Bustard (Ardeotis nigriceps): The Great Indian Bustard is another significant endangered species in India, with only around 150 individuals remaining in the wild. These large birds have suffered due to habitat loss, hunting, and disturbances caused by infrastructural development.
4. Red Panda (Ailurus fulgens): The adorable red panda, found in the northeastern parts of India, is threatened by habitat loss, poaching, and the illegal wildlife trade. It is estimated that there are fewer than 10,000 red pandas left in the wild.
5. Gangetic Dolphin (Platanista gangetica): The Gangetic dolphin is a freshwater dolphin found in the Ganges and Brahmaputra river systems. Its population has declined due to pollution, habitat fragmentation, and bycatch in fishing nets. Only around 3,000 individuals are believed to remain.
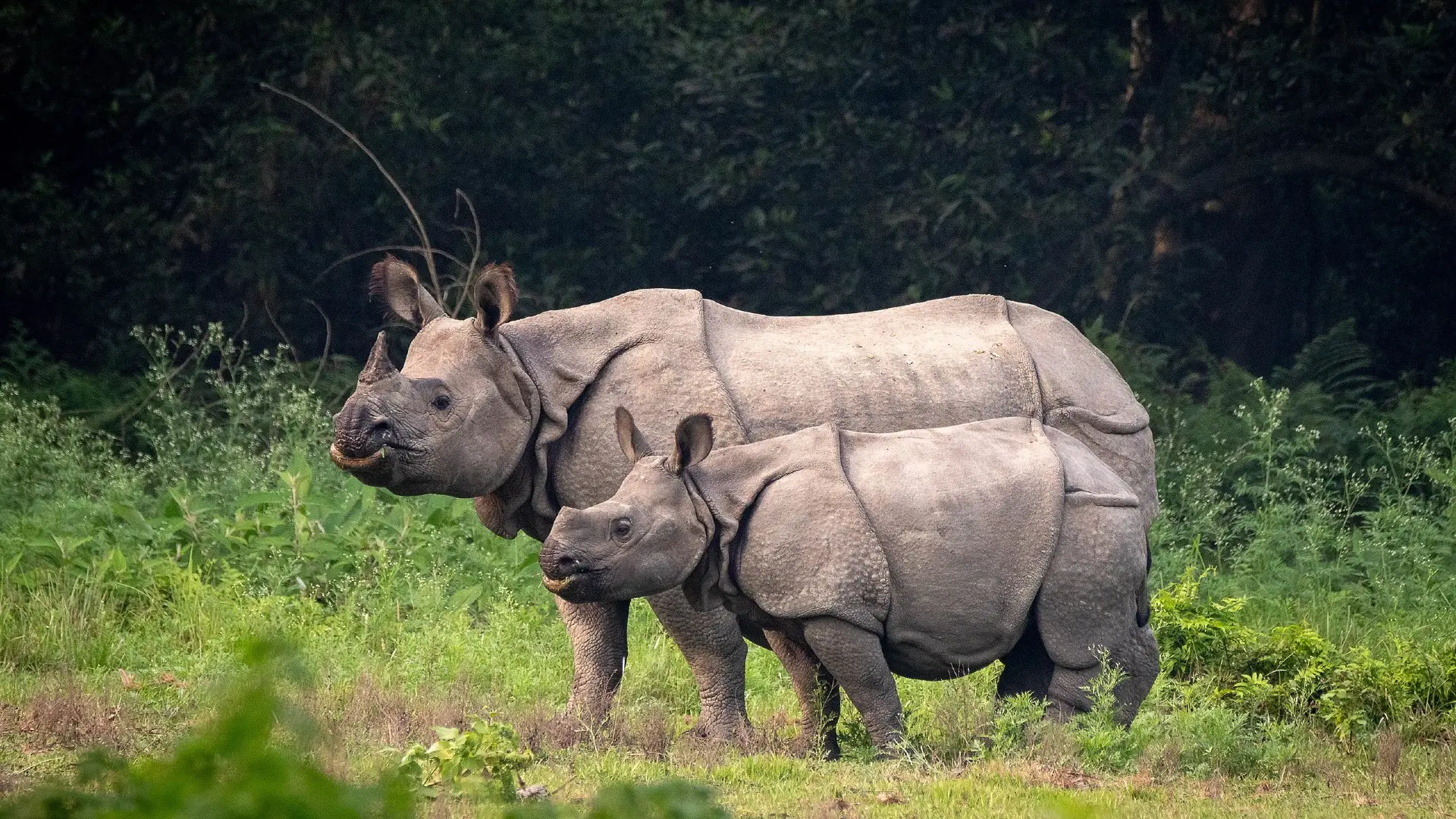
6. The One-Horned Rhino: The mighty one-horned rhinoceros, once widespread across the subcontinent, is now restricted to a few pockets in Assam and Uttar Pradesh. These gentle giants are targeted by poachers for their horns, which are mistakenly believed to have medicinal properties.
The Threats: A Delicate Web of Challenges
Habitat loss is a primary culprit behind the decline of in the population of endangered species in India. Ever-expanding human settlements, infrastructure projects, and agricultural practices lead to fragmentation and destruction of vital wildlife corridors. Poaching for body parts used in traditional medicine or for illegal wildlife trade fuels the endangerment of many animals like rhinos and tigers.
The conflict between humans and wildlife is another major concern. As human populations grow, competition for resources intensifies. Predators like tigers may be seen as threats to livestock, leading to retaliatory killings. Accidental entanglement in fishing gear and infrastructure projects like dams further endanger aquatic species.
Climate change presents a new and looming threat for these critically endangered species in India. Rising temperatures, erratic weather patterns, and changes in precipitation all disrupt the delicate balance of ecosystems, impacting the habitats and food sources of endangered species.
Government Efforts to Protect Endangered Species in India:
The Indian government has implemented several initiatives to protect and conserve endangered species:
- Project Tiger: Launched in 1973, Project Tiger is a flagship conservation program aimed at protecting the Bengal tiger and its natural habitats. It has established numerous tiger reserves across the country.
- Project Elephant: Initiated in 1992, Project Elephant focuses on the conservation and management of Asian elephants, another major endangered species in India. It focuses on preserving their habitats and addressing human-elephant conflicts.
- Project GIB : SC proposed "Project GIB," a project similar to Project Tiger that would conserve the Great Indian Bustard. State governments have been directed by the project guidelines to install bird diverters in priority regions where birds reside and, whenever possible, convert overhead electric wires into underground power cables.
A three-person team led by physicist Rahul Rawat, scientist Sutirtha Dutta, and deputy director of the Corbett Foundation Devesh Gadhavi was also established by the top court to evaluate the viability of installing high-voltage underground power connections.
- Wildlife Protection Act, 1972: This act provides a legal framework for the protection of wildlife and their habitats, regulating hunting, trade, and other activities that may harm endangered species in India.
- National Biodiversity Action Plan: This plan outlines strategies and actions for the conservation and sustainable use of biodiversity in India.
- Establishment of Protected Areas: India has a network of national parks, wildlife sanctuaries, and biosphere reserves dedicated to the protection of endangered species and their habitats.
How Can We Contribute?
As individuals, we can play a crucial role in the conservation of endangered species in India:
- Support Conservation Organizations: Donate or volunteer with organizations working towards the protection of endangered species and their habitats.
- Reduce, Reuse, and Recycle: Minimize your ecological footprint by adopting sustainable practices, such as reducing waste, conserving energy, and recycling.
- Raise Awareness: Educate others about the importance of biodiversity and the plight of endangered species. Engage in community events, campaigns, and social media initiatives to spread awareness.
- Responsible Tourism: When visiting natural areas, follow guidelines and regulations to minimize disturbance to wildlife and their habitats.
- Sustainable Consumption: Be mindful of the products you purchase and consume. Avoid products derived from endangered species in India or those that contribute to habitat destruction.
- Support Sustainable Livelihoods: Promote and support initiatives that provide alternative, sustainable livelihoods for communities living in or near protected areas, reducing their dependence on exploiting natural resources.
Data & Facts on Endangered Species in India
According to the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List, there are currently around 38,500 species threatened with extinction globally, including 10,964 species in India.
India is home to 8% of the world's biodiversity, including many unique and endemic species.
Habitat loss and degradation are the primary threats to 85% of all endangered species in India described on the IUCN Red List.
Poaching and illegal wildlife trade have decimated the populations of iconic species like elephants, rhinos, and tigers.
Climate change is projected to become one of the leading drivers of biodiversity loss in the coming decades, exacerbating the threats faced by endangered species.
Conclusion
The conservation of endangered species in India is not only crucial for maintaining the ecological balance but also for preserving our rich natural heritage. We must understand that the fight to save India's endangered species is a marathon, not a sprint. While the Indian government has taken significant steps to protect these species, individual actions and collective efforts are paramount in ensuring their survival. By raising awareness, supporting conservation organizations, and adopting sustainable practices, we can all contribute to a future where these magnificent creatures continue to thrive in their natural habitats.
Let us all become champions for wildlife conservation, and together, we can rewrite the narrative for endangered species in India, ensuring their survival for generations to come.
Read more in Environment
May 27, 2025
TUI Staff
May 27, 2025
TUI Staff

Stay Tuned with The United Indian!
Our news blog is dedicated to sharing valuable and pertinent content for Indian citizens. Our blog news covering a wide range of categories including technology, environment, government & economy ensures that you stay informed about the topics that matter most. Follow The United Indian to never miss out on the latest trending news in India.
©The United Indian 2024