The United Indian

India is a land of varied cultures and magnificent geographical terrains, and it is also one of the bio diverse zones. From the mighty tiger of Bengal to the shy one-horned Rhinoceros of the Assam, the forests of India buzz with the rhythm of life. However, this symphony is under threat. Globally, deforestation, meaning cutting down trees in large areas, is slowly erasing these valuable habitats, often referred to as the sound of silence.
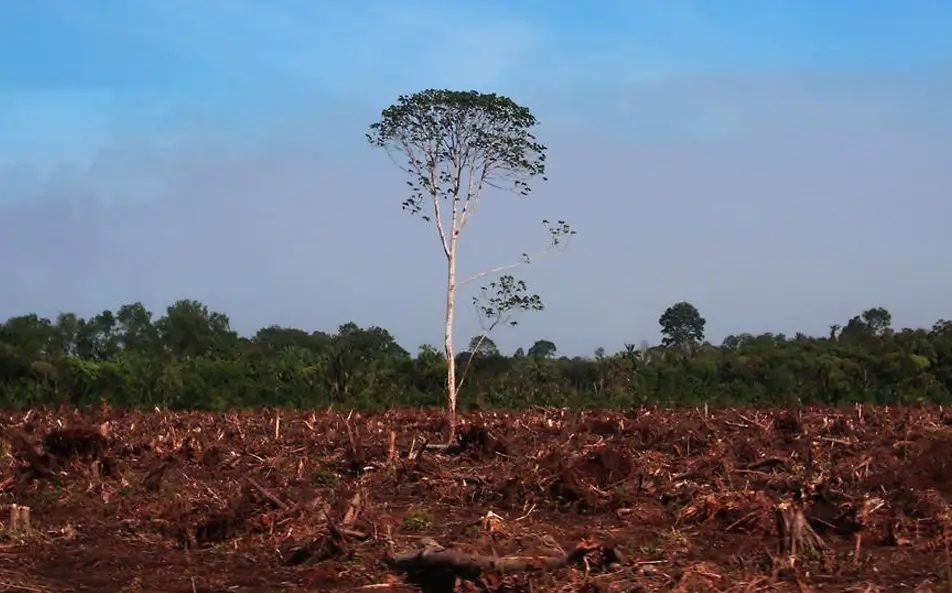
The process of removing forest cover on a large scale is now a global concern that is commonly referred to as deforestation. In India this is even more noticeable because of the vast and diverse wildlife in the country. India’s geographical location offer various ecosystems including Himalayan mountain ranges and tropical rain forests and this makes the country to host diverse wildlife. Unfortunately, the continued destruction of habitats for human use exposes them to significant risks that may harm flora and fauna. Focusing on the problem of deforestation and its effects on wildlife in India, this article describes the causes and effects of deforestation, as well as possible ways to eliminate this problem.
Causes of Deforestation in India
- Agricultural Expansion: Among the main reasons for deforestation in India, one of the most significant is the conversion of forested areas into agricultural land. As the population gets large, the population needs food for survival, this leads to increased deforestation to provide for crop and grazing land for animals.
- Urbanization and Infrastructure Development: Population growth and increased infrastructure development for things like roads, highways, and industrial development contribute to heavy deforestation. It becomes clear that the creation of cities and towns threatens the existence of forests.
- Logging and Timber Harvesting: Illegal logging and the demand for timber and wood products contribute to deforestation. Despite regulations, illicit activities persist, causing considerable damage to forest cover.
- Mining Activities: India’s rich mineral resources lead to extensive mining activities, particularly in forested areas. The extraction of minerals like coal, bauxite, and iron ore often results in large-scale deforestation and habitat destruction.
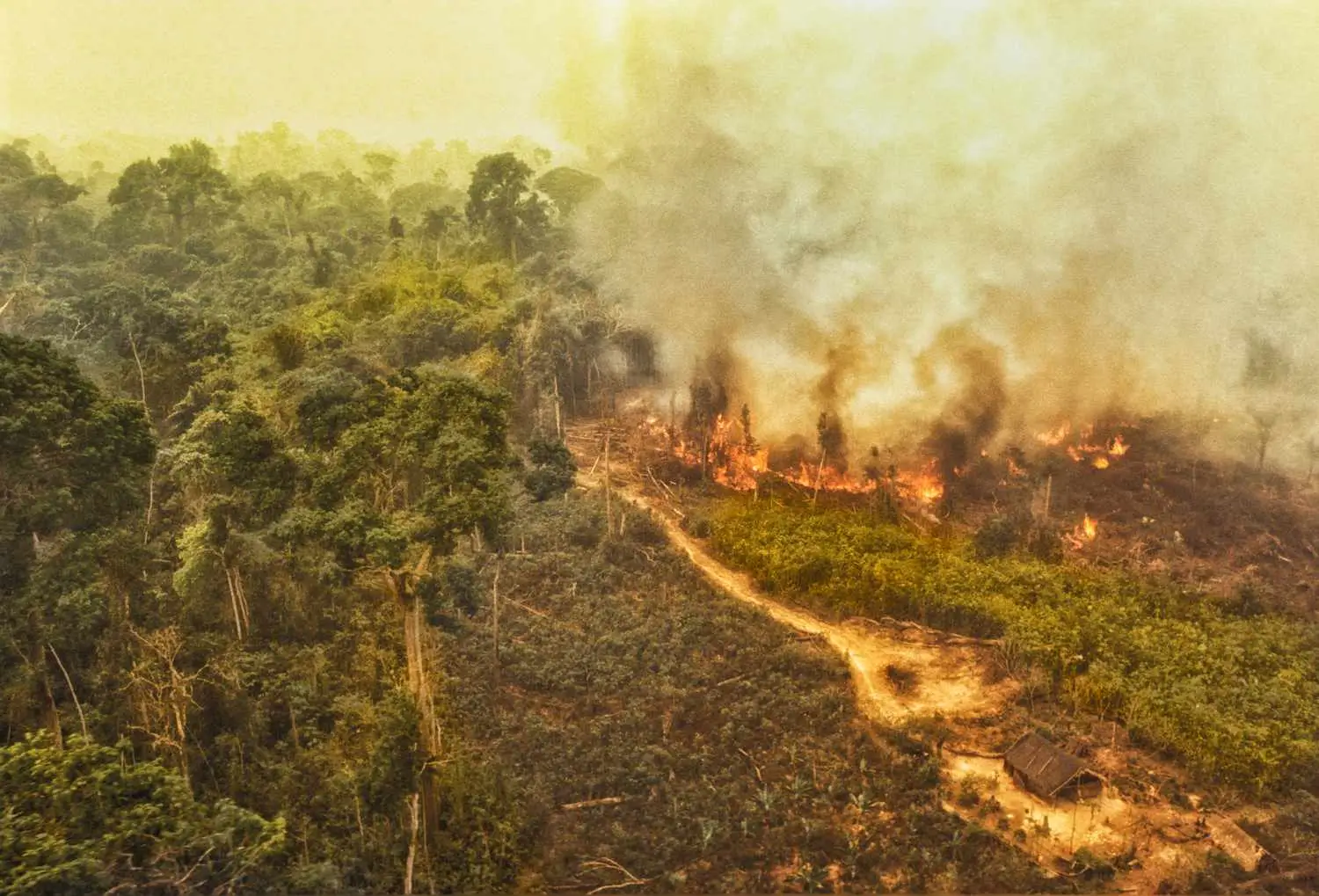
- Forest Fires: Both natural and human-induced forest fires play a role in deforestation in India. In many cases, fires are deliberately set to clear land for agriculture or other purposes, exacerbating the loss of forest cover.
Consequences of Deforestation on Indian Wildlife
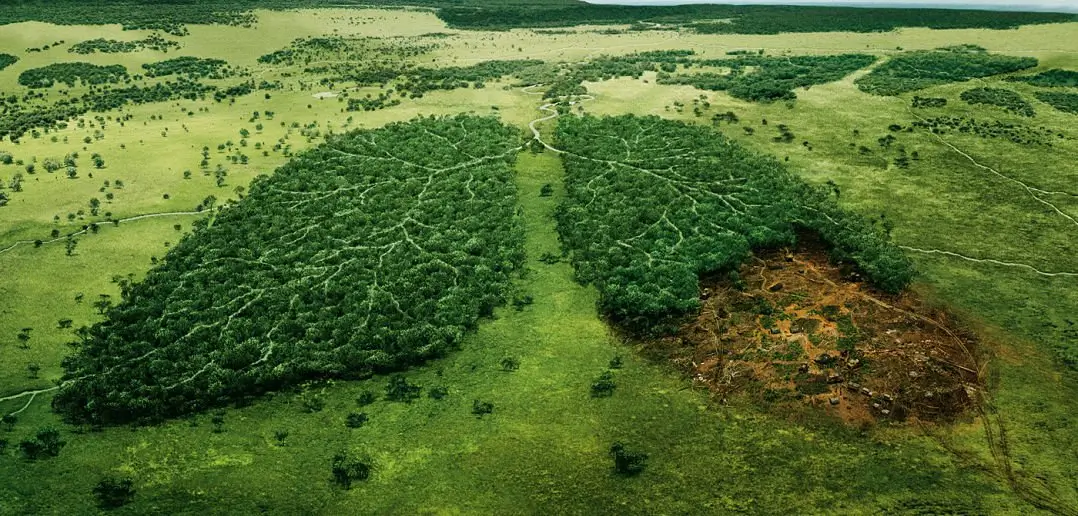
1. Habitat Loss and Fragmentation : Forests are not merely clusters of trees; they are intricate webs connecting life. Deforestation leads to the direct loss of habitats, leaving many species without shelter and resources. Habitat fragmentation, where large continuous forests are broken into smaller patches, isolates wildlife populations. This fragmentation hinders gene flow and breeding, leading to reduced genetic diversity and increased vulnerability to diseases and environmental changes.
2. Decline in Biodiversity : India is one of the 17 megadiverse countries, home to a vast array of species. However, as one of the major impacts of deforestation in India, it has threatened this biodiversity. Species that cannot adapt to new environments or migrate to other habitats face the risk of extinction. Iconic species like the Bengal tiger, Asiatic elephant, and Indian rhinoceros are particularly affected, as they require large territories to thrive.
3. Disruption of Ecosystem Services : Forests provide numerous ecosystem services, including carbon sequestration, water regulation, and soil conservation. Deforestation disrupts these services, leading to soil erosion, altered water cycles, and increased greenhouse gas emissions. The loss of these services affects not only wildlife but also human communities that rely on forests for their livelihoods.
4. Increased Human-Wildlife Conflict : As forests shrink, wildlife is forced to move closer to human settlements in search of food and habitat. This proximity often leads to increased human-wildlife conflicts, with animals raiding crops, preying on livestock, and, in some cases, attacking humans. These conflicts result in economic losses for local communities and often lead to retaliatory killings of wildlife.
5. Climate Change : climate change is one of the significant impacts of deforestation in India. by releasing stored carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. Climate change, in turn, affects wildlife through altered weather patterns, shifting habitats, and changes in the availability of food and water. Species that are unable to adapt to these rapid changes face heightened risks of decline and extinction.
Case Studies
1. The Sundarbans Mangrove Forest
The Sundarbans, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, is the largest mangrove forest in the world and a critical habitat for the Bengal tiger. Deforestation in this region, driven by agricultural expansion and urban development, has led to significant habitat loss. The resulting habitat fragmentation has put the tiger population under severe stress, with reduced prey availability and increased human-tiger conflicts.
2. Western Ghats
The Western Ghats, a biodiversity hotspot, is home to numerous endemic species. Deforestation for plantations, agriculture, and infrastructure projects has fragmented habitats, threatening species like the Nilgiri tahr and the lion-tailed macaque. Conservation efforts are to control deforestation in India are ongoing, but the pressure from human activities continues to challenge the survival of these unique species.
Conservation Efforts and Solutions for Deforestation In India
1. Protected Areas and Wildlife Sanctuaries
Establishing protected areas, national parks, and wildlife sanctuaries is crucial for conserving habitats and species. India has made significant strides in this direction, with several well-managed protected areas. However, expanding and effectively managing these areas is essential to mitigate the impact of deforestation.
2. Afforestation and Reforestation
Afforestation (planting new forests) and reforestation (restoring degraded forests) are vital strategies to combat deforestation. Initiatives like the National Afforestation Programme aim to increase forest cover and restore ecosystems. Community involvement in these efforts can enhance their effectiveness and ensure sustainable outcomes.
3. Sustainable Agriculture and Land Use Practices
Promoting sustainable agricultural practices, such as agroforestry, can reduce the pressure on forests. Agroforestry integrates trees and shrubs into agricultural systems, providing benefits like soil conservation, enhanced biodiversity, and improved livelihoods for farmers.
4. Strengthening Legal Frameworks and Enforcement
Strengthening laws and regulations related to forest conservation and wildlife protection is crucial. Ensuring strict enforcement of these laws, along with combating illegal logging and mining activities, can significantly reduce deforestation in India.
5. Community-Based Conservation
Engaging local communities in conservation efforts is key to long-term success. Community-based conservation programs that provide economic incentives for sustainable practices can help reduce deforestation. Involving indigenous communities, who have traditional knowledge of forest management, can also enhance conservation outcomes.
6. Education and Awareness
Raising awareness about the importance of forests and the impact of deforestation on wildlife is vital. Educational programs and campaigns can help foster a conservation ethic among the public, encouraging more sustainable behaviors and support for conservation initiatives.
What Can We Do? A Call to Action
The future of India's wildlife rests on our shoulders. Here's how we can all play a part:
- Reduce, Reuse, Recycle: Our everyday choices have a ripple effect. Reducing paper consumption and opting for recycled products helps lessen the demand for wood pulp, a major driver of deforestation.
- Be a Conscious Consumer: Many products, like furniture and paper, use wood from unsustainable sources. Research and choose companies committed to responsible forestry practices.
- Support Conservation Efforts: Numerous organizations are working tirelessly to protect India's wildlife. Donate or volunteer your time to make a difference.
- Spread Awareness: Educate others about the impact of deforestation. The more people who understand the gravity of the situation, the stronger the movement for change becomes.
Conclusion
Deforestation in India poses a severe threat to Indian wildlife, with far-reaching consequences for biodiversity, ecosystem services, and human communities. Addressing this challenge requires a multifaceted approach, including the establishment of protected areas, sustainable land use practices, legal enforcement, and community engagement. By implementing these strategies, India can work towards conserving its rich natural heritage and ensuring a sustainable future for its wildlife and people.
The preservation of forests and wildlife is not just an environmental issue but also a crucial aspect of India’s cultural and economic well-being. Protecting these natural resources is imperative for maintaining ecological balance and securing the livelihoods of millions who depend on forests. Through concerted efforts and a collective commitment to conservation, the impact of deforestation on Indian wildlife can be mitigated, paving the way for a healthier and more resilient environment.
Read more in Environment
May 27, 2025
TUI Staff
May 27, 2025
TUI Staff

Stay Tuned with The United Indian!
Our news blog is dedicated to sharing valuable and pertinent content for Indian citizens. Our blog news covering a wide range of categories including technology, environment, government & economy ensures that you stay informed about the topics that matter most. Follow The United Indian to never miss out on the latest trending news in India.
©The United Indian 2024